1989. Maximum matching
Graph (V, E) is called bipartite, if
its set of vertices V can be divided to two subsets A and B so
that any edge from E connects vertex from A with vertex
from B.
The matching P is any
subset E such that no its two edges have common vertex.
Maximum matching is a matching where the
number of edges is maximal.
Find the maximal matching in the bipartite
graph.
Input. The first line contains three numbers n, m and k (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 100, 1 ≤
k ≤ 10000), where n is a number of vertices in a
set A, m is a number of vertices in a set B, and k
is a number of edges in a graph. Each of the next k lines contains two
numbers ui and vi, meaning that a vertex ui
from set A is connected with an edge with vi from
set B. The vertices in sets A and B are numbered
separately, starting from one. All given numbers are integers.
Output. Print in the first line the number of edges l in
maximal matching. Then print l rows, two numbers in each. The numbers aj
and bj in the j-th row mean
that matching includes the edge between vertex aj of the
set A and a vertex bj of the set B. Printed
edges must form a maximum matching.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
2 3 41 11 22 2
2 3 |
2 1 1 2 3 |
SOLUTION
graphs - maximum matching
Algorithm analysis
This is a classical
maximum matching problem, which can either be reduced to flows on a graph, or
solved using the augmenting path algorithm.
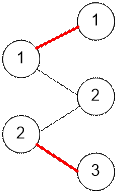
Example
The input graph
and maximum matching has the form:
Algorithm realization
Consider the augmenting path algorithm
without optimization. The graph is stored in the adjacency list g. To mark the visited vertices during the depth first search, use the array used. To store the
current matching, use the array mt.
#define MAX 110
vector<vector<int>
> g;
vector<int> used, mt;
The function dfs
finds the
augmenting path from v with depth first search and returns 1 if such path is
found. If an increasing chain is found, the matching is alternated along it.
int dfs(int v)
{
if (used[v]) return
0;
used[v] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i
< g[v].size(); i++)
{
int to = g[v][i];
if (mt[to] == -1 || dfs(mt[to]))
{
mt[to] = v;
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
Finding the maximum matching.
void AugmentingPath(void)
{
Initially the current matching is empty.
mt.assign (m+1, -1);
Start searching for an augmenting path from each vertex of the left part. Set to zero the array of
visited vertices used.
for (int i = 1; i
<= n; i++)
{
used.assign(n+1,
0);
dfs(i);
}
}
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&m,&k);
g.resize(n+1);
for(i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
g[a].push_back(b);
}
Find and print the value of the maximum matching.
AugmentingPath();
for (flow = 0, i = 1; i <= m; i++)
if (mt[i] != -1) flow++;
printf("%d\n",flow);
Print the maximum matching itself.
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
if (mt[i] != -1) printf("%d
%d\n",mt[i],i);
Algorithm realization – optimization
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace
std;
vector<vector<int> > g;
vector<int> used, mt, par;
int i, j, ptr;
int n, m, k, a, b, flow;
int dfs(int
v)
{
if (used[v]) return 0;
used[v] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < g[v].size(); i++)
{
int to =
g[v][i];
if (mt[to]
== -1 || dfs(mt[to]))
{
mt[to] = v;
par[v] = to;
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
void AugmentingPath(void)
{
int i, run;
mt.assign (m+1, -1);
par.assign (n+1, -1);
for (run = 1;
run; )
{
run = 0; used.assign(n+1, 0);
for (i = 1;
i <= n; i++)
if
((par[i] == -1) && dfs(i)) run = 1;
}
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d %d
%d",&n,&m,&k);
g.resize(n+1);
for(i = 0; i
< k; i++)
{
scanf("%d
%d",&a,&b);
g[a].push_back(b);
}
AugmentingPath();
for (flow =
0, i = 1; i <= m; i++)
if (mt[i]
!= -1) flow++;
printf("%d\n",flow);
for (i = 1; i
<= m; i++)
if (mt[i]
!= -1) printf("%d %d\n",mt[i],i);
return 0;
}